- What is the WordPress Backend?
- Key Components of the WordPress Backend
- Posts and Pages
- Media Library
- Appearance
- Plugins
- Settings
- Backend Settings and Customization
- WordPress Backend Development Overview
- WordPress Content Management
- Advanced WordPress Backend Customization
- Security Considerations for the WordPress Backend
- Tools for Managing the WordPress Backend Efficiently
- Common WordPress Backend Issues and Troubleshooting
- Why Invest in Professional WordPress Backend Development?
- Mastering the WordPress Backend: Your Key to Success
Whether you’re a beginner, developer, or agency, mastering the WordPress backend can significantly enhance your ability to create powerful and efficient websites. It will help you create, manage or customize a WordPress site. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the intricacies of the WordPress backend, exploring its features, functionalities, and the art of WordPress backend development.
What is the WordPress Backend?
The WordPress backend is the control center of your WordPress website. Sometimes also referred to as the WordPress dashboard or admin panel. From there you can manage content, customize your site’s appearance, and control various settings that affect your site’s functionality.
Unlike the frontend, which visitors see when they browse your website, the WordPress backend is accessible only to authorized users with login credentials. This secure area is where you can:
- Create and edit posts and pages
- Manage media files
- Install and configure plugins and themes
- Adjust site settings
- Manage user roles and permissions
The WordPress backend is designed to be user-friendly, allowing even those with minimal technical knowledge to manage their websites effectively. However, its depth and flexibility also provide ample opportunities for advanced users and developers to create highly customized and powerful web solutions.
WordPress Development Agency
Experience WordPress development with our custom-coded websites. Perfect for agencies, our reliable service ensures timely delivery and client satisfaction.
Key Components of the WordPress Backend
WordPress Dashboard
When you first log in to the WordPress backend, you’re greeted by the dashboard. This central hub provides an overview of your site’s activity and quick access to common tasks. Key elements of the dashboard include:
- WordPress News: Keeps you updated with the latest WordPress news and events
- At a Glance: Shows the number of posts, pages, and comments on your site
- Activity: Displays recent comments and content updates
- Quick Draft: Allows you to quickly start a new post

Admin Panel
The admin panel is the heart of the WordPress backend. Here, you’ll find various sections for managing your site:
- Posts: Create, edit, and manage blog posts
- Pages: Create and manage static pages
- Media: Upload and organize images, videos, and other files
- Comments: Moderate and manage user comments
- Appearance: Customize your site’s look with themes and widgets
- Plugins: Extend your site’s functionality with plugins
- Users: Manage user accounts and permissions
- Tools: Import/export content and perform site health checks
- Settings: Configure various WordPress backend settings
Let’s explore some of these key areas in more detail:
Posts and Pages
The Posts and Pages sections are where you create and manage your site’s content. The main difference is that Posts are typically used for blog entries and are displayed in reverse chronological order, while Pages are for static content like “About Us” or “Contact” pages.
In both sections, you’ll find:
- Settings for categories, tags, and featured images
- A list of existing content
- Options to add new content
- The WordPress editor (Gutenberg or Classic, depending on your setup)
Media Library
The Media Library is where you manage all the files you’ve uploaded to your WordPress site. Here, you can:
- Insert media into your posts and pages
- Upload new files
- Organize files into folders
- Edit image metadata (alt text, captions, etc.)

Appearance
The Appearance section is where you control the look and feel of your website. Key features include:
- Theme Editor: Edit your theme’s files directly (use with caution)
- Themes: Install and customize your site’s theme
- Customize: Fine-tune your theme’s settings
- Widgets: Add and arrange widgets in your sidebars and footer
- Menus: Create and manage navigation menus

Plugins
The Plugins section allows you to extend the functionality of your WordPress site. Here, you can:
- Install new plugins
- Activate or deactivate plugins
- Update plugins
- Configure plugin settings

Settings
The Settings section is where you configure various WordPress backend settings that control how your site operates. Key areas include:
- Permalinks: Configure your URL structure
- General: Set your site title, tagline, and other basic information
- Writing: Configure default post settings
- Reading: Set your homepage display and RSS feed options
- Discussion: Manage comment settings
- Media: Set default sizes for image uploads

Backend Settings and Customization
General Settings
In the General Settings section, you can configure the fundamental aspects of your site:
- Site Title and Tagline: These appear in various places, including the browser tab and search results
- WordPress Address (URL) and Site Address (URL): Ensure these are correctly set for proper site functioning
- Email Address: Used for admin notifications
- Time Zone and Date Format: Affects how dates are displayed on your site
Permalink Structure
Permalinks are the permanent URLs to your individual pages and blog posts. A well-structured permalink can improve your site’s SEO. To set your permalink structure:
- Go to Settings > Permalinks
- Choose a permalink structure (e.g., Post name, Day and name, Custom structure)
- Click “Save Changes”

Managing User Roles and Permissions
WordPress offers several default user roles, each with different levels of access and permissions:
- Administrator: Full access to all features
- Editor: Can publish and manage posts, including those of other users
- Author: Can publish and manage their own posts
- Contributor: Can write and manage their posts but cannot publish them
- Subscriber: Can only manage their profile
To manage user roles:
- Go to Users > All Users
- Click on a user to edit their profile
- In the “Role” dropdown, select the appropriate role
- Click “Update User”

WordPress Backend Development Overview
WordPress backend development involves customizing and extending the core functionality of WordPress. This can include:
- Creating custom themes and plugins
- Modifying the admin interface
- Developing custom post types and taxonomies
- Integrating with external APIs
Developers use languages like PHP, JavaScript, HTML, and CSS to create custom solutions tailored to specific needs.
Setting Up a Development Environment
To get started with WordPress backend development:
- Install a local server environment (e.g., XAMPP, MAMP, or Local by Flywheel)
- Install WordPress locally
- Set up a code editor (e.g., Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text)
- Install version control software (e.g., Git)
Introduction to Child Themes
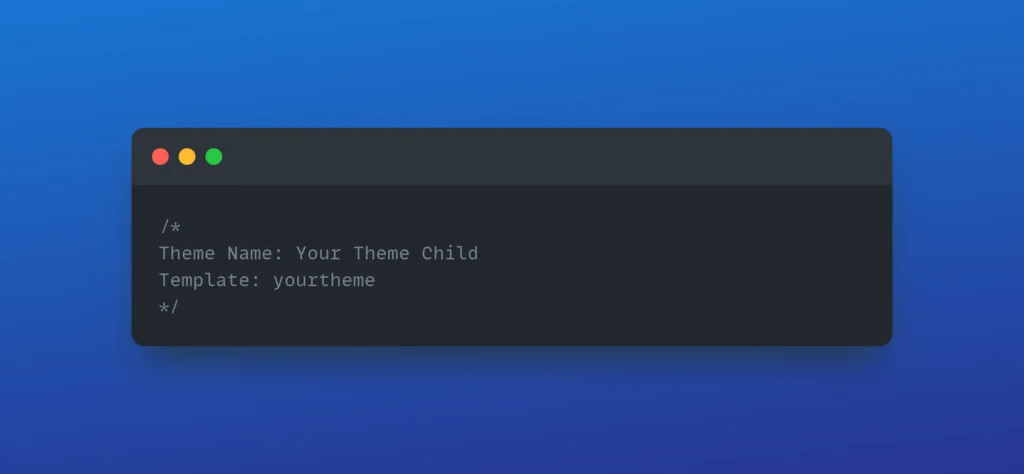
Child themes allow you to modify an existing theme without losing your changes when the parent theme is updated. To create a child theme:
- Create a new folder in your themes directory (e.g.,
yourtheme-child) - Create a
style.cssfile with the following header:
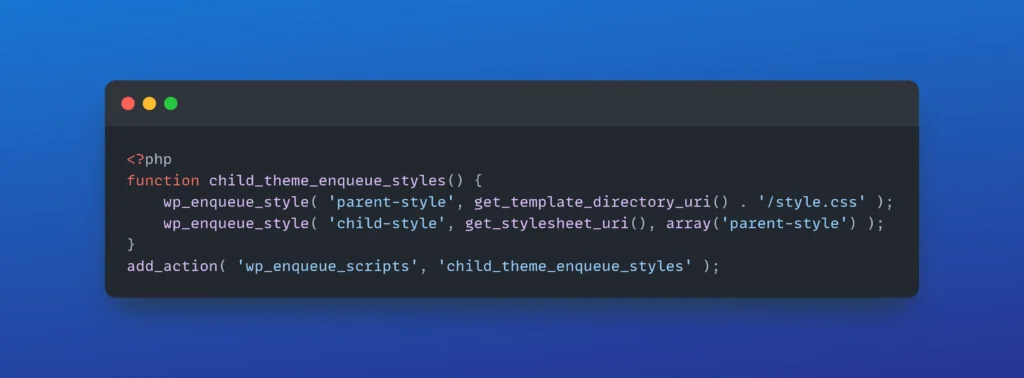
- Create a
functions.phpfile to enqueue the parent and child theme styles:
WordPress Content Management
At its core, WordPress is a content management system (CMS). The WordPress backend provides powerful tools for WordPress content management, including:
- A user-friendly editor for creating and formatting content
- The ability to schedule posts for future publication
- Tools for managing categories and tags
- Options for controlling comments and discussions
The introduction of the Gutenberg editor has revolutionized content creation in WordPress, allowing for more flexible and visually appealing layouts. Gutenberg uses “blocks” for different types of content, which can be customized and arranged as needed.
Advanced WordPress Backend Customization
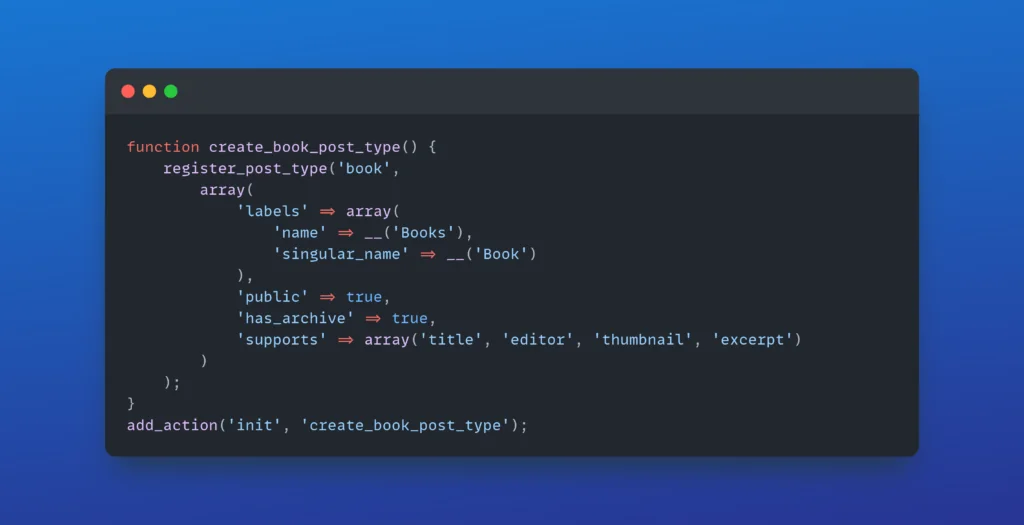
Custom Post Types and Taxonomies
Custom post types allow you to create content types beyond the default posts and pages. Here’s an example of how to register a custom post type:
Customizing the Admin Dashboard
You can add custom widgets to the WordPress dashboard to provide quick access to important information:

Security Considerations for the WordPress Backend
Securing your WordPress backend is crucial for protecting your site from potential threats. Some key security measures include:
- Use strong passwords and two-factor authentication: Implement a policy for strong passwords and consider using a plugin for two-factor authentication.
- Limit login attempts: Use a plugin or custom code to limit the number of failed login attempts.
- Keep WordPress core, themes, and plugins updated: Regularly update all components of your WordPress installation to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Implement SSL encryption: Use HTTPS for your entire site, including the backend.
- Use security plugins: Consider using reputable security plugins for additional protection.
Here’s an example of how you might limit login attempts using code:

Tools for Managing the WordPress Backend Efficiently
- WP-CLI: A command-line interface for WordPress that allows you to manage many aspects of your WordPress installation.
- Advanced Custom Fields: A plugin that allows you to add custom fields and content types easily.
- Yoast SEO: Helps optimize your content for search engines directly from the backend.
- UpdraftPlus: An excellent backup solution to safeguard your site’s data and settings.
- Query Monitor: A developer tool for debugging database queries, PHP errors, hooks and actions, block editor blocks, enqueued scripts and stylesheets, HTTP API calls, and more.
Common WordPress Backend Issues and Troubleshooting
- White Screen of Death (WSOD): Often caused by a PHP error. Enable WP_DEBUG in wp-config.php to see error messages.
- Unable to access wp-admin: Could be due to incorrect file permissions or .htaccess issues. Check your file permissions and try regenerating your .htaccess file.
- Slow admin panel: Can be caused by too many plugins, large databases, or server issues. Try deactivating plugins one by one to identify the culprit.
- Database connection errors: Check your wp-config.php file for correct database credentials.
Why Invest in Professional WordPress Backend Development?
While WordPress is user-friendly, investing in professional WordPress backend development can yield significant benefits:
- Custom Solutions: Tailored functionality to meet specific business needs
- Enhanced Performance: Optimized code for faster load times
- Improved Security: Custom security measures to protect your site
- Scalability: Solutions that grow with your business
- Improved Workflow: Customized admin interfaces for more efficient content management
- Integration: Seamless connection with other business systems and APIs
Professional developers can create complex custom post types, taxonomies, and meta boxes, implement advanced security measures, and optimize database queries for improved performance. They can also develop custom plugins and themes that perfectly align with your business needs and branding.
Projects
Outsource WordPress projects with confidence. We provide fixed-price white-label development and dedicated management with no upfront payment.
Mastering the WordPress Backend: Your Key to Success
The WordPress backend is more than just a control panel; it’s the engine that powers your website. By mastering its features and understanding the potential of WordPress backend development, you can create websites that are not only visually appealing but also powerful, secure, and efficient.
Whether you’re just starting out or looking to take your WordPress skills to the next level, investing time in learning the ins and outs of the WordPress backend will pay dividends in your ability to create and manage successful websites. From basic content management to advanced customization and development, the WordPress backend offers a world of possibilities for creating outstanding web experiences.
Remember, the journey to mastering the WordPress backend is ongoing. As WordPress evolves, stay updated with the latest developments, best practices, and security measures. If you would like expert guidance, contact us today.






