- Understanding WordPress Development: Key Concepts
- Getting Started with WordPress Development
- WordPress Themes and Templates
- Custom Theme Development
- WordPress Plugins: Extending Functionality
- WordPress Development Agency
- WordPress Website Development Process
- Essential WordPress Development Tools and Resources
- WordPress Security Best Practices
- WordPress SEO: Optimizing for Search Engines
- Advanced Customization and Development Techniques
- Best Practices for Launching and Maintaining a WordPress Website
- Custom WordPress Development
- Your Next Steps in WordPress Development
- FAQs
WordPress has firmly established itself as the world’s leading content management system (CMS), powering over 40% of all websites on the internet. Its versatility and user-friendly interface make it the top choice for anyone looking to build a robust online presence. Whether you’re creating a simple blog or a complex e-commerce site, WordPress offers unparalleled ease of use, flexibility, and scalability, allowing both beginners and seasoned developers to tailor websites to their needs.
This guide is designed for a wide range of users – developers looking to master advanced techniques, business owners wanting to understand their site’s capabilities, and beginners who are just getting started with WordPress. No matter where you are on your journey, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the tools and knowledge to get the most out of WordPress.

Understanding WordPress Development: Key Concepts
At its core, WordPress development refers to the process of creating, customizing, and maintaining websites using the WordPress platform. This can range from designing and implementing themes to developing custom plugins or optimizing performance. WordPress development allows you to transform the basic framework into a tailored website that meets the specific needs of a business, individual, or organization.
What is WordPress Development?
Defining WordPress Website Development
WordPress website development involves building a fully functional website using the tools, features, and flexibility that WordPress offers. This can encompass everything from selecting a theme, configuring essential plugins, and setting up the site’s structure to advanced tasks like custom coding for unique design elements or functionality. Developers can use WordPress as a starting point to create websites that are responsive, secure, and scalable.
WordPress as a CMS: Core Concepts
WordPress stands out as a content management system (CMS) due to its open-source nature, which means anyone can use, modify, and distribute it for free. It is built on PHP and MySQL, and its modular design allows users to extend functionality with plugins and customize appearance with themes. Some of the core concepts of WordPress include:
- Themes: Control the appearance and layout of the website.
- Plugins: Add or extend functionality to meet specific needs.
- Widgets: Provide additional content and features in various areas of the site.
- Posts and Pages: Core content types used to create blogs or static pages.
By understanding these fundamental elements, users can manage and enhance their WordPress sites more effectively.
WordPress.org vs. WordPress.com: Differences and Which One to Choose
Many users are initially confused by the two versions of WordPress: WordPress.org and WordPress.com. While both allow you to create websites, they serve different needs:
- WordPress.org: Known as the “self-hosted” version, WordPress.org gives users complete control over their website. You can choose your hosting provider, install custom themes and plugins, and have full flexibility over the site’s design and functionality. This version is ideal for developers, businesses, and anyone looking for full customization and scalability.
- WordPress.com: This is a hosted platform that takes care of hosting and management for you. While it’s easier to set up, it offers limited flexibility and customization options compared to WordPress.org. It’s a good choice for beginners or those who don’t require extensive customization but comes with paid plans for additional features.
Choosing between the two depends on your goals. If you want complete control over your site’s development, WordPress.org is the better option. For simplicity and managed hosting, WordPress.com may suit your needs.
Front-end vs. Back-end Development in WordPress
WordPress development can be divided into two primary areas: front-end and back-end development.
- Front-end development: Focuses on what users see and interact with on a website. This includes working with themes, CSS, HTML, and JavaScript to create the visual design and ensure responsiveness across devices.
- Back-end development: Deals with the behind-the-scenes infrastructure that makes the site functional. This involves working with PHP, databases, and server configurations to ensure that the site’s core functionalities operate smoothly. Back-end developers may also work on developing or customizing plugins to add more features.
Both front-end and back-end developers play crucial roles in building and maintaining a successful WordPress website.

Getting Started with WordPress Development
Starting with WordPress development requires setting up a proper environment where you can build, test, and optimize your website before making it live. This section will guide you through the essential tools and steps to get your development environment up and running.
Setting Up Your Development Environment
Before diving into WordPress development, it’s important to establish a development environment that allows you to safely experiment and build your website without impacting a live site. A solid setup will help streamline your workflow, catch potential issues early, and ensure smooth deployment.
Local Development Tools (XAMPP, MAMP, Local by Flywheel)
Local development tools let you create a WordPress site on your own computer without needing a live server. These tools simulate the necessary server environment and are perfect for development and testing. Some popular options include:
- XAMPP: A free, cross-platform solution that allows you to create a local server environment using Apache, MySQL, and PHP.
- MAMP: Similar to XAMPP, MAMP is available for macOS and Windows and provides a quick setup for local WordPress development.
- Local by Flywheel: A user-friendly tool designed specifically for WordPress development. It allows you to quickly spin up WordPress sites locally with features like SSL and one-click staging.
These tools give you the flexibility to develop your WordPress site offline, make changes safely, and only move your work to a live server when it’s ready.
Hosting and Server Requirements for WordPress Development
When working with WordPress, whether locally or on a live server, you need to ensure your hosting environment meets the minimum requirements. WordPress is built with PHP and requires a MySQL or MariaDB database. Here are the key requirements:
- PHP version: 7.4 or greater
- MySQL version: 5.7 or greater OR MariaDB version 10.3 or greater
- HTTPS support
Many hosting providers offer WordPress-specific hosting plans optimized for performance, security, and scalability. Ensure that your host supports these minimum requirements to avoid any technical issues during development.
Staging vs. Production Environments
When working on WordPress development, it’s critical to understand the difference between staging and production environments:
- Staging environment: A staging environment is a clone of your live site where you can test new features, updates, and plugins without affecting your live website. It’s an essential part of the development process, ensuring that your changes are safe to deploy.
- Production environment: This is the live version of your site that users visit. All changes should be thoroughly tested in the staging environment before being pushed to production to prevent downtime or unexpected issues.
A good WordPress development workflow will include both environments to ensure seamless updates and improvements to the website.
WordPress Installation & Setup
Once your development environment is ready, you can move forward with installing WordPress. There are two main ways to install WordPress: using one-click installation options provided by hosting providers or manually installing it on your local server.
One-Click Installation Options (cPanel, Softaculous)
Most modern hosting providers offer one-click WordPress installation tools, such as cPanel with Softaculous. These options make setting up WordPress extremely easy by automating the process of downloading, setting up databases, and configuring the core files. Simply log into your hosting account, navigate to the one-click installer, and follow the prompts to install WordPress within minutes.
Manual Installation on Localhost
If you’re setting up WordPress for local development using tools like XAMPP, MAMP, or Local by Flywheel, you may opt for a manual installation. Here’s a quick overview of the process:
- Download WordPress: Visit the official WordPress.org site and download the latest version.
- Extract and move files: Unzip the WordPress files and place them in the appropriate folder in your local server directory (e.g., htdocs for XAMPP).
- Create a database: Access phpMyAdmin (or your local equivalent) and create a new database for WordPress.
- Run the installation: Open your browser and navigate to
http://localhost/your-folder-name/. You’ll be prompted to complete the WordPress setup by entering database information and creating an admin account.
With the manual method, you have full control over your local environment, ideal for custom WordPress development projects.

WordPress Themes and Templates
At the heart of WordPress development lies the concept of themes. A WordPress theme is a collection of files that controls the overall look and layout of your website. It dictates everything from the design of your homepage to the styling of individual blog posts and pages. Themes allow users to easily switch the appearance of their site without altering the underlying content, offering immense flexibility to customize the user experience.
Themes control many aspects of your site’s appearance, including:
- Layout: Determines how content is arranged, whether in grids, single columns, or more complex designs.
- Fonts and colors: Specifies typography and color schemes for consistency in design.
- Widgets and sidebars: Defines placement and availability of widgets or sidebars for additional features.
- Responsiveness: Adjust the website’s layout to display correctly on different screen sizes.
Popular Theme Marketplaces and Frameworks
There are thousands of free and premium themes available across the web, making it easy to find a theme that fits your needs. Some of the most popular marketplaces and frameworks for WordPress themes include:
- ThemeForest: A popular marketplace offering premium WordPress themes across various categories and industries.
- WordPress Theme Repository: A large collection of free themes maintained by WordPress.org, ideal for users starting out.
- Genesis Framework: A robust framework for WordPress development, offering a strong foundation for creating custom child themes with built-in security and SEO features.
These marketplaces provide an abundance of options, from fully customizable premium themes to simple, free alternatives.
Custom Theme Development
For developers looking to create a fully unique website, custom theme development offers endless possibilities. A custom theme allows you to control every element of your site’s appearance and functionality. Whether you’re developing a theme from scratch or customizing an existing one, you’ll need a strong understanding of WordPress’s theme structure and core files.
Child Themes: What They Are and Why They Matter
Child themes are essential for developers who want to modify an existing theme without losing updates and support. A child theme inherits the functionality and styling of a parent theme but allows for customizations in a separate file, ensuring that updates to the parent theme won’t overwrite your custom changes. This is especially useful for making small tweaks to a theme’s design or adding specific features without creating a full custom theme.
Creating Your First Custom Theme (Step-by-Step Guide)
Developing your own custom theme starts with understanding how WordPress structures its themes. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Create a theme folder: In your WordPress wp-content/themes directory, create a new folder for your custom theme.
- Create the style.css file: This file contains the theme’s metadata and styling rules. At the top of the file, you need to add a theme header comment with details such as the theme name, version, and author.
- Create the index.php file: This is the default template file that displays your site’s homepage content.
- Add additional template files: You can now create key template files like header.php, footer.php, and sidebar.php to structure the various sections of your site.
- Activate the theme: Once you have the core files in place, go to your WordPress dashboard, navigate to “Appearance > Themes,” and activate your new custom theme.
Key Theme Files
A WordPress theme is composed of various files that work together to create the site’s structure and design. Some of the key theme files include:
- header.php: Contains the code for the header section of the site, including the site’s logo, navigation, and meta tags.
- footer.php: Manages the footer section, where you typically include copyright information, links, or additional navigation.
- functions.php: A powerful file used to add custom features and functions to the theme, such as enabling new widget areas or registering navigation menus.
- style.css: Defines the visual appearance of your site through CSS rules, determining everything from typography to layout.
These files form the backbone of your theme and can be customized to create virtually any design or functionality you need.
Best Practices for Responsive Design and Mobile Optimization
In today’s mobile-first world, responsive design is no longer optional. It’s crucial to ensure that your WordPress theme adapts seamlessly to different screen sizes and devices. Some best practices for achieving responsive design include:
- Use fluid grids: Design with relative units (like percentages) instead of fixed widths to ensure layouts adjust across devices.
- Flexible images: Ensure that images scale appropriately by using CSS rules like
max-width:100%to prevent them from overflowing their containers. - Media queries: Use media queries in your CSS to apply specific styles based on device size, ensuring an optimized experience for mobile users.
- Test on multiple devices: Always test your theme on a range of devices and browsers to ensure a consistent experience.
By adhering to these best practices, you can create a theme that offers a smooth and visually appealing experience, whether users are on desktops, tablets, or smartphones.

WordPress Plugins: Extending Functionality
What Are Plugins and Why They Matter?
Plugins are small software components that integrate seamlessly with your WordPress site to add features such as contact forms, SEO tools, security enhancements, and more. Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced developer, plugins are essential for building a highly functional website without reinventing the wheel. By leveraging existing plugins, you can save time, improve efficiency, and offer unique capabilities to your users.
Installing, Activating, and Managing Plugins
Installing and managing plugins in WordPress is a simple and straightforward process. Here’s how you can get started:
- Search for Plugins: From your WordPress dashboard, navigate to the “Plugins” section and click “Add New.” You can search for plugins based on functionality or browse the most popular and recommended ones.
- Install the Plugin: Once you find the plugin you need, click “Install Now.”
- Activate the Plugin: After installation, you will see an option to “Activate” the plugin. Once activated, the plugin’s functionality will become available on your site.
- Manage Settings: Many plugins offer customization options. After activation, go to the plugin’s settings page (usually found under “Settings” or “Tools”) to configure it according to your preferences.
Regularly updating and managing your plugins is essential for security and performance. It’s also a good practice to deactivate or delete any plugins you’re no longer using to keep your site optimized.
Free vs. Premium Plugins: When to Invest
One of the great advantages of WordPress development is the wide range of both free and premium plugins available. While free plugins are often sufficient for basic functionality, premium plugins offer advanced features, better support, and regular updates. So when should you invest in premium plugins?
- Free Plugins: Ideal for small websites or simple tasks. The WordPress Plugin Directory has thousands of free plugins that are reliable and regularly updated. However, support may be limited.
- Premium Plugins: Often the better choice for larger or more complex websites that require advanced functionality, such as eCommerce, membership management, or custom forms. Premium plugins usually come with dedicated support, more frequent updates, and enhanced security features.
Investing in premium plugins is worthwhile when the functionality you need isn’t covered by free options, or when you require robust support and regular updates to keep your site running smoothly.
Building Custom WordPress Plugins
If existing plugins don’t fully meet your needs, you can develop your own custom WordPress plugin. Custom plugins allow you to create tailored features and integrations for your website, offering a higher level of flexibility and control over its functionality.
Step-by-Step Guide to Developing a Plugin
Developing a custom WordPress plugin requires a clear understanding of WordPress’s plugin structure. Here’s a simple step-by-step guide:
- Create a Plugin Folder: In your WordPress directory (wp-content/plugins), create a new folder with a unique name for your plugin.
- Create the Main PHP File: Inside your plugin folder, create a PHP file (e.g., my-plugin.php) and add the following plugin header comment:
- Add Functions: Now you can start adding functions and features to your plugin. These functions can range from adding new shortcodes to creating custom post types.
- Activate the Plugin: Once your plugin file is ready, you can activate it from the WordPress dashboard under the “Plugins” section.
Key Files and Coding Standards
When building a custom plugin, it’s important to follow WordPress coding standards to ensure that your plugin is secure, maintainable, and compatible with other WordPress components. Here are the key files you may include in your plugin:
- Main plugin file: The primary PHP file that contains the core functionality of your plugin.
- Additional PHP files: You can create additional files for specific features or functions to keep your code organized.
- Readme.txt: A file that provides information about your plugin, its version, and usage instructions. This is particularly useful if you plan to distribute your plugin.
- CSS and JS files: If your plugin includes front-end elements, you may need additional stylesheets or JavaScript files.
WordPress coding standards recommend using best practices like proper file organization, following naming conventions, and ensuring compatibility with other plugins and themes.
Best Practices for Plugin Performance
To maintain optimal performance and avoid conflicts, it’s important to follow best practices when developing or using plugins:
- Limit the Number of Plugins: Installing too many plugins can slow down your site’s performance. Stick to essential plugins and avoid duplicates that perform similar tasks.
- Test for Compatibility: Ensure that your plugins are compatible with the latest version of WordPress and don’t conflict with other plugins or themes.
- Use Hooks and Filters: Instead of modifying core files, use WordPress hooks and filters to extend functionality in a modular way.
- Optimize Code for Speed: Write efficient code and avoid loading unnecessary scripts or styles. Ensure that your plugin doesn’t negatively affect page load times.
By following these best practices, you can ensure that your plugins are not only functional but also optimized for performance, providing a better experience for your users.
WordPress Development Agency
Experience WordPress development with our custom-coded websites. Perfect for agencies, our reliable service ensures timely delivery and client satisfaction.
WordPress Website Development Process
Creating a successful WordPress website involves a step-by-step approach that ensures both functionality and user experience. From planning and wireframing to designing and building the site architecture, every phase plays a critical role in delivering a smooth, user-friendly website. In this section, we’ll explore the essential steps for developing a well-structured WordPress site.
Planning and Wireframing
Before diving into WordPress development, it’s essential to plan and wireframe your site. This involves gathering client requirements or defining your own site goals. Wireframing helps visualize the layout and structure of your website, ensuring a clear roadmap before development. Tools like Figma, Adobe XD, or Balsamiq are great for creating simple wireframes tailored for WordPress sites.
Building the Site Architecture
A solid site structure is key to user experience and SEO. WordPress organizes content through pages, posts, categories, and tags. Understanding this hierarchy is crucial for building a well-structured website. A clear navigation system should guide visitors smoothly through your content, helping them find what they need quickly.
Design and UX Best Practices
When designing your WordPress site, tools like Elementor and Divi make it easy to create professional layouts without coding. Focus on mobile-first design to ensure your site works well on all devices. To improve the user experience, keep navigation simple and intuitive and maintain a clean, clutter-free layout that enhances readability and accessibility.
Essential WordPress Development Tools and Resources
To make the WordPress development process smoother and more efficient, it’s important to have the right tools and resources at your disposal. Below are some key tools that can help you throughout your WordPress development journey.
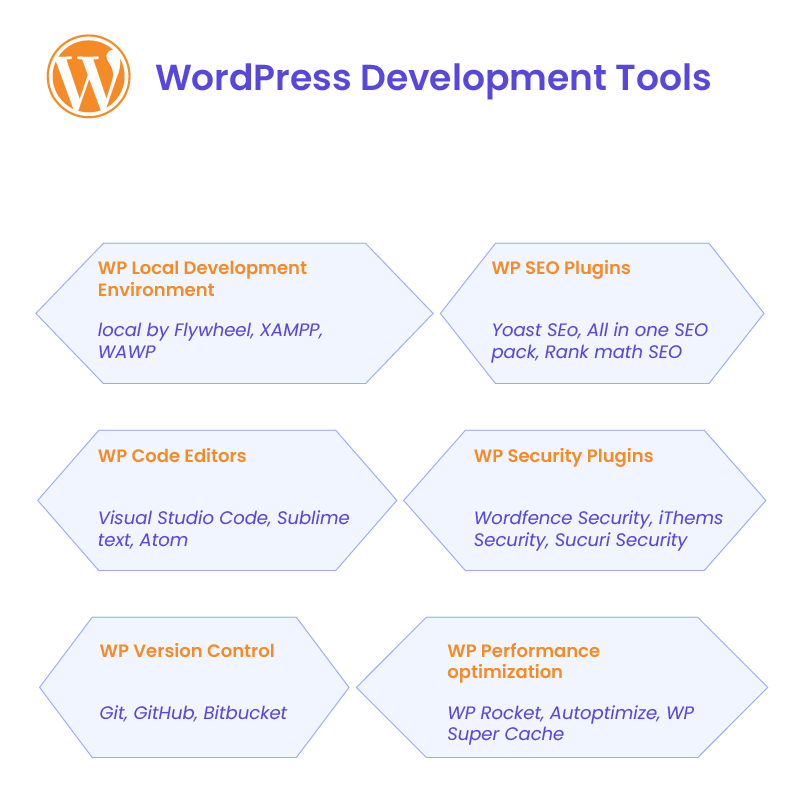
Code Editors (Sublime Text, Visual Studio Code)
A good code editor is essential for writing clean and efficient code. Sublime Text and Visual Studio Code (VS Code) are two popular choices among WordPress developers. Sublime Text is lightweight and fast, while VS Code offers a wide range of extensions, including those tailored for WordPress development. Both allow you to write, edit, and debug code easily.
WordPress CLI (Command Line Interface)
The WordPress Command Line Interface (WP-CLI) is a powerful tool for managing WordPress websites directly from the command line. With WP-CLI, you can perform tasks like installing plugins, updating WordPress core, managing users, and even backing up your site – all without using the WordPress dashboard. It’s a must-have tool for developers looking to streamline their workflow.
Debugging Tools and Performance Testers
To ensure your WordPress site runs smoothly, you need reliable debugging and performance tools. Query Monitor helps you track database queries, PHP errors, and other performance issues. For speed optimization, GTmetrix allows you to analyze your website’s loading time and get actionable insights to improve performance.
GitHub and Version Control for WordPress Projects
Using GitHub for version control is essential in managing changes and collaborating on WordPress projects. With Git, you can track every modification to your codebase, roll back to previous versions if necessary, and collaborate with other developers more effectively.
WordPress Documentation and Development Resources
WordPress offers extensive official documentation to help you learn everything from basic theme development to advanced plugin creation. Other valuable resources include the WordPress Developer Handbook, WordPress forums, and community-driven blogs where developers share tips, tutorials, and best practices.

WordPress Security Best Practices
Keeping your WordPress website secure is crucial to protecting your site from hackers, malware, and data breaches. Here are some essential best practices to follow to ensure your WordPress site remains safe.
Common Vulnerabilities in WordPress Websites
Like any website platform, WordPress is susceptible to security vulnerabilities if not properly maintained. Common vulnerabilities include outdated plugins, weak passwords, and unpatched themes. Hackers often exploit these weak points, so it’s important to stay proactive by regularly updating your site and strengthening security measures.
Security Plugins (Wordfence, Sucuri)
Installing a reliable security plugin is one of the simplest ways to protect your site. Wordfence and Sucuri are two of the most popular WordPress security plugins. They provide features like malware scanning, firewall protection, and real-time threat monitoring. Both plugins help you detect and prevent security threats before they cause damage to your website.
SSL, HTTPS, and Firewall Integration
Securing your site with SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is essential for encrypting the connection between your website and its visitors. This is especially important if your site handles sensitive information like payments. Enabling HTTPS and integrating a firewall further strengthens security by adding an extra layer of protection from external threats and unauthorized access.
Regular Backups and Updates
Regularly backing up your website ensures you have a copy of your site’s data in case of a security breach or other issues. Additionally, keeping WordPress core, themes, and plugins up to date is crucial, as updates often include important security patches. A tool like UpdraftPlus can automate backups, making the process simple and worry-free.
WordPress SEO: Optimizing for Search Engines
Optimizing your WordPress site for search engines is essential for improving visibility and driving organic traffic. Here are the key SEO strategies to implement for your WordPress website.
On-Page SEO: Meta Tags, Alt Text, Permalinks
On-page SEO involves optimizing individual pages to help search engines understand and rank your content. This includes adding meta tags (title and description), using alt text for images to describe them to search engines, and setting SEO-friendly permalinks (URLs) that are short and descriptive. These elements improve both user experience and search engine indexing.
SEO Plugins
SEO plugins like Yoast SEO and Rank Math make optimizing your WordPress site simple. They provide guidance on how to improve your content, manage meta tags, and generate XML sitemaps. These plugins also analyze readability, keyword density, and other SEO factors, making it easier to optimize each page for search engines.
Website Speed Optimization and Caching Plugins
A fast-loading website improves both user experience and search engine rankings. Plugins like WP Rocket or W3 Total Cache help speed up your site by caching static content, reducing server load, and optimizing file delivery. Website speed is a critical factor in search engine optimization.
Integrating Google Analytics and Search Console
To track your site’s SEO performance, integrate Google Analytics and Google Search Console. Google Analytics helps you monitor traffic and user behavior, while Search Console provides insights into how your site is performing in search results and alerts you to any SEO issues.

Advanced Customization and Development Techniques
For those ready to take their WordPress development to the next level, advanced customization techniques offer a wide range of possibilities to build powerful, feature-rich websites.
WordPress APIs and REST API Integration
WordPress offers a variety of APIs that enable developers to extend functionality and integrate external services. The WordPress REST API is particularly powerful, allowing you to create, update, and delete WordPress data programmatically. This API makes it possible to build custom applications and connect WordPress with other platforms, making it ideal for developers looking to create highly customized, data-driven websites.
WooCommerce Development
WooCommerce is the go-to plugin for creating e-commerce websites with WordPress. Setting up WooCommerce is straightforward – after installation, you’ll need to configure basic settings like payment gateways, shipping methods, and tax options. Beyond the default setup, you can create custom WooCommerce themes and plugins to offer unique shopping experiences tailored to your brand or client’s needs.
Custom Post Types and Taxonomies
WordPress isn’t limited to just pages and posts. You can create custom post types (CPTs) to manage different kinds of content, such as portfolios, products, or testimonials. Pairing CPTs with custom taxonomies allows you to organize and categorize your content in a way that fits your site’s structure, offering enhanced flexibility for complex content management.
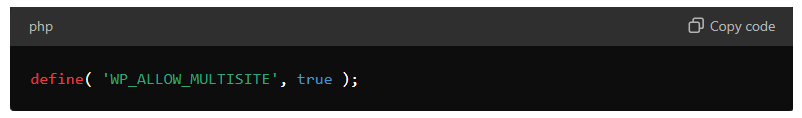
Multisite Development
If you need to manage multiple websites from a single WordPress installation, WordPress Multisite is the solution. With multisite, you can create and manage a network of sites under one dashboard. This is particularly useful for organizations or businesses that operate multiple websites, as it simplifies management and maintenance.
Best Practices for Launching and Maintaining a WordPress Website
Launching and maintaining a WordPress website involves careful planning and ongoing attention to ensure it remains functional, secure, and fast. Here are some best practices to follow.
Pre-Launch Checklist
Before going live, it’s important to run through a pre-launch checklist:
- Check for broken links using tools like Broken Link Checker.
- Test site speed with services like GTmetrix or Google PageSpeed Insights to ensure fast load times.
- Conduct security checks to confirm that your site is protected from potential vulnerabilities.
How to Make a WordPress Site Live
To make your WordPress site live, you’ll need to connect your website to a domain name and set up hosting. Many hosting providers offer easy-to-follow steps to migrate your site from a development environment to a live server, ensuring a smooth transition.
Ongoing WordPress Maintenance
After launching, regular maintenance is key to keeping your site secure and functional. This includes:
- Regular backups using plugins like UpdraftPlus to safeguard your data.
- Updating WordPress core, plugins, and themes to ensure your site runs smoothly.
- Security scans with tools like Wordfence or Sucuri to monitor and block potential threats.
Performance Monitoring Tools
To ensure optimal performance, use monitoring tools like UptimeRobot or Pingdom to track website downtime, page load times, and overall site health. These tools provide insights that help you proactively address any issues.
Custom WordPress Development
Custom WordPress Development tailored to your needs. Unique designs, expert solutions, and seamless functionality for a standout website. Learn more!
Your Next Steps in WordPress Development
WordPress development is a step-by-step process that starts with planning and wireframing, followed by setting up your development environment, choosing themes and plugins, and implementing advanced customization. Along the way, it’s essential to prioritize security, SEO, and performance optimization to build a successful website.
The journey doesn’t stop at launch – ongoing maintenance and regular updates are key to keeping your WordPress site secure and running smoothly. WordPress offers endless opportunities to learn and experiment, from creating custom themes to developing plugins and integrating third-party APIs. As you continue to explore, there are plenty of resources available
such as blogs, tutorials, and developer communities, to support your growth in WordPress development.At The White Label Agency, we specialize in providing expert WordPress development services, from custom website builds to ongoing maintenance, ensuring your site meets the highest standards. Contact us today to discuss how we can help with your WordPress development needs.
FAQs
What is WordPress development?
WordPress development refers to the process of building, customizing, and managing websites using the WordPress platform. It includes creating custom themes and plugins, modifying site architecture, and optimizing performance. Developers use languages like PHP, JavaScript, HTML, and CSS to extend WordPress functionality and meet specific needs for businesses or personal projects.
How much does WordPress development cost?
The cost of WordPress development varies depending on the project scope. For a simple site, costs can range from $500 to $2,000, while more complex custom sites can cost upwards of $10,000 or more. Prices depend on the level of customization, the developer’s expertise, and whether additional services like SEO or ongoing maintenance are included.
How to get started with WordPress development?
To start with development, you’ll need a solid understanding of HTML, CSS, PHP, and JavaScript. Begin by setting up a local development environment with tools like Local by Flywheel, install WordPress, and start experimenting with themes and plugins. Numerous online resources, including tutorials, courses, and guides, can help beginners build their skills step-by-step.
What tools do I need for WordPress development?
The essential tools for development include:
Local Development Environment: Tools like XAMPP or Local by Flywheel.
Code Editor: Visual Studio Code or PHPStorm for writing and managing code.
Version Control: Git to track code changes.
WP-CLI: A command-line tool to manage WordPress installations, plugins, and themes.
What are the best practices for maintaining a WordPress website?
To maintain a WordPress website, follow these best practices:
Regular Updates: Keep WordPress core, plugins, and themes up to date.
Security Measures: Implement strong passwords, SSL certificates, and security plugins like Wordfence.
Backups: Schedule regular backups using tools like UpdraftPlus.
Performance Optimization: Optimize images, enable caching, and clean up the database regularly to keep the site fast and efficient.







