- Why Choosing the Right CMS Matters
- Background and Evolution: Drupal vs WordPress
- User Experience & Usability: Drupal vs WordPress
- Customization, Flexibility & Functionality
- Performance, Scalability & Hosting
- Drupal to WordPress Migration
- Security & Stability: Drupal vs WordPress
- SEO & Content Optimization: Drupal vs WordPress
- Community, Support & Learning Resources
- Cost & Total Cost of Ownership
- Ideal Use Cases & Business Considerations
- Website as a service
- Future Outlook & Trends
- Final Verdict & Recommendations
- Drupal vs WordPress – Which One is Right for You?
When building a website, one of the most critical decisions is choosing the right content management system (CMS). Your CMS determines how easily you can create, manage, and scale your website, impacting everything from user experience to security and long-term costs. In the ongoing debate of WordPress vs Drupal, both platforms offer powerful features, but they cater to different user needs.
Why Choosing the Right CMS Matters
Selecting the wrong CMS can lead to technical limitations, increased development costs, and challenges in website management. Businesses, developers, and organizations must evaluate usability, flexibility, performance, and security before making a decision.
- WordPress – Originally designed as a blogging platform, has evolved into the most widely used CMS, powering over 40% of all websites. It is known for its user-friendly interface, extensive plugin ecosystem, and flexibility for small businesses, bloggers, and large enterprises.
- Drupal – A more developer-centric CMS is renowned for its robustness, scalability, and ability to handle complex websites. It offers advanced customization options, making it the preferred choice for government agencies, universities, and large organizations with intricate content structures.
This guide is designed for a wide range of readers, including beginners, developers, and enterprise decision-makers. For beginners, this comparison provides a straightforward breakdown of Drupal vs WordPress, helping them understand which platform suits their needs without requiring technical expertise. For developers, this guide offers a deeper look into the customization capabilities, coding flexibility, and advanced features of both platforms. For enterprise decision-makers, this guide provides insights into scalability, security, and long-term website management.
By the end, you will have a clear understanding of the differences between Drupal and WordPress, allowing you to make an informed decision based on your specific website goals, technical capabilities, and long-term objectives.
Background and Evolution: Drupal vs WordPress

Both WordPress and Drupal have evolved significantly over the years, shaping the web development landscape in different ways. While WordPress started as a simple blogging platform and gradually became the most widely used content management system (CMS), Drupal has remained a powerful choice for complex, large-scale websites that require advanced customization and security. Understanding the history and growth of these platforms provides valuable insight into their strengths, market positioning, and ideal use cases.
WordPress: From Blogging to the World’s Leading CMS
WordPress was first introduced in 2003 by Matt Mullenweg and Mike Little as a user-friendly blogging platform built on PHP and MySQL. Designed to make publishing content easy, it quickly gained popularity due to its intuitive interface and open-source nature. Over the years, it evolved into a full-fledged CMS, powering websites of all sizes, from small personal blogs to large enterprise sites.
Today, WordPress dominates the CMS market, with over 40% of all websites running on the platform. Its vast library of themes and plugins allows users to create and customize websites with minimal coding knowledge. Supported by a massive global community, WordPress continues to grow, offering extensive documentation, forums, and resources for both beginners and developers.
Drupal: Built for Complex, High-Performance Websites
Drupal was launched in 2001 by Dries Buytaert as a message board system before evolving into a powerful CMS. Unlike WordPress, Drupal was designed from the start to handle complex website structures, making it a preferred choice for large organizations, government agencies, and educational institutions.
Drupal’s modular architecture gives developers extensive control over site functionality, making it a flexible yet technically demanding CMS. While it does not have the same widespread adoption as WordPress, it remains the go-to choice for websites that require advanced security, scalability, and performance. Many prestigious organizations, including NASA, Harvard University, and The White House, have chosen Drupal for their web presence due to its robust framework and ability to manage large amounts of structured content.
Drupal vs WordPress: Evolution and Market Adoption
The WordPress vs Drupal debate continues as both platforms serve distinct audiences. WordPress has established itself as the most accessible CMS, ideal for businesses, bloggers, and developers who need a user-friendly and highly customizable solution. On the other hand, Drupal remains a preferred option for enterprise-level websites that demand advanced functionality and strict security measures.
Despite their differences, both platforms continue to evolve, driven by active communities and ongoing improvements. Whether prioritizing ease of use or technical sophistication, understanding the Drupal vs WordPress evolution helps users choose the best CMS for their needs.
User Experience & Usability: Drupal vs WordPress
When choosing a CMS, user experience plays a crucial role in determining how easily website administrators, content creators, and developers can manage their websites. In the WordPress vs Drupal debate, both platforms offer different approaches to usability. While WordPress prioritizes simplicity and accessibility for non-developers, Drupal provides a more structured and developer-centric experience.
Administrative Interface & Dashboard
One of the most noticeable differences is the administrative interface.
- WordPress Dashboard: WordPress is designed with user-friendliness in mind. Its admin panel features an intuitive dashboard that allows users to manage content, install plugins, and customize themes effortlessly. The interface is clean, with easy navigation menus, a visual editor for content creation, and quick access to essential settings. Even beginners can start publishing content with minimal training.
- Drupal Admin Interface: Drupal’s backend is more complex and geared towards experienced users. While it provides robust content management tools, the interface is not as visually intuitive as WordPress. Drupal’s admin panel requires more configuration and familiarity with its terminology, which can be challenging for non-technical users. However, it offers a structured and flexible system for managing complex content hierarchies and permissions.
Learning Curve
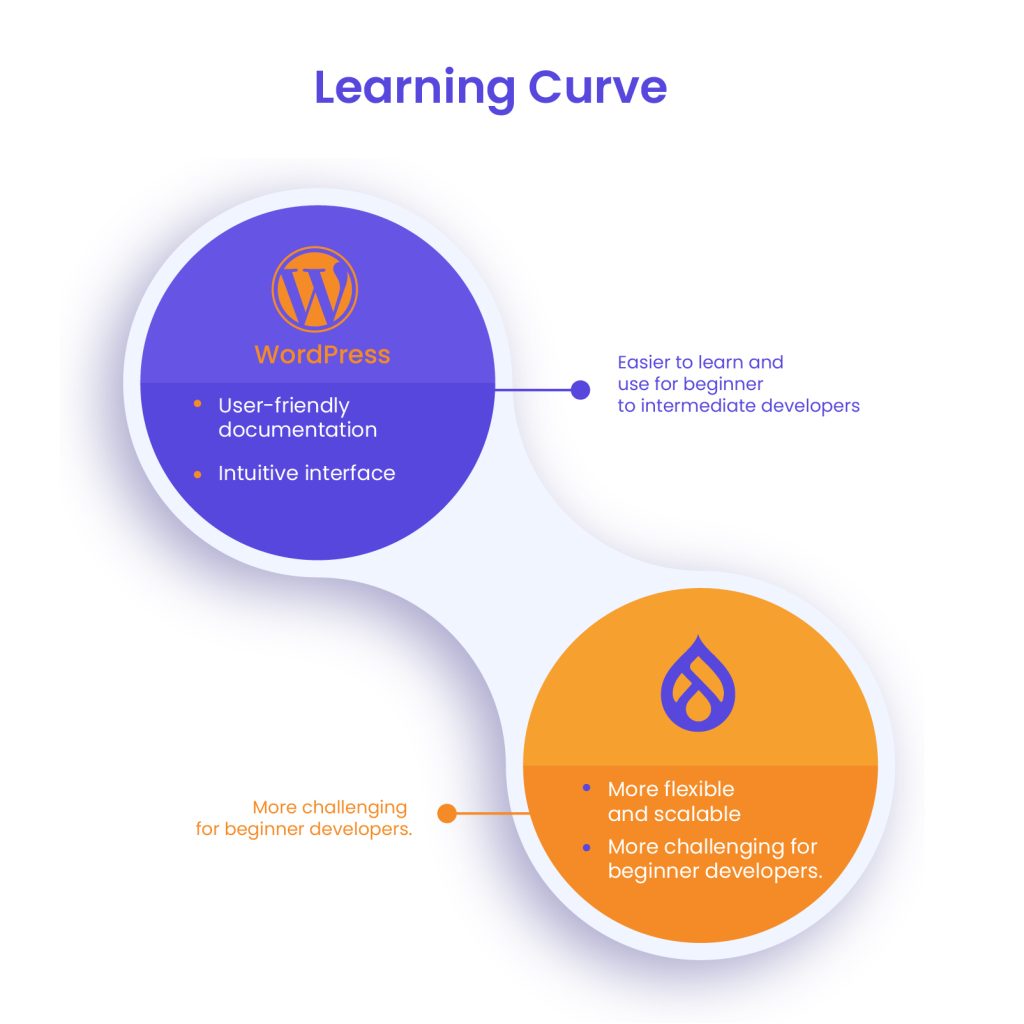
The learning curve is a significant factor in the WordPress vs Drupal comparison.
- WordPress: Known for its ease of use, WordPress allows beginners to set up and manage websites quickly. With thousands of ready-made themes and plugins, users can build functional websites without any coding knowledge. The block-based Gutenberg editor further simplifies content creation, making it accessible to non-developers.
- Drupal: Drupal has a steeper learning curve due to its modular approach and advanced settings. Unlike WordPress, which provides a plug-and-play experience, Drupal requires users to manually configure many aspects of their site. While this offers greater flexibility and control, it can be overwhelming for those without a technical background. However, developers appreciate Drupal’s robust framework, which allows for greater scalability and custom content types.
Content Management Workflow
Both WordPress and Drupal excel in content management, but their workflows differ.
- WordPress: WordPress simplifies content creation with its visual editor, allowing users to write, edit, and publish posts easily. It includes built-in media management, categories, and tags for organizing content. The addition of block-based editing (Gutenberg) enhances flexibility, making content structuring more dynamic.
- Drupal: Drupal is designed for handling large volumes of structured content. It provides powerful content types, taxonomies, and views that allow users to create sophisticated content architectures. Unlike WordPress, Drupal does not come with a built-in WYSIWYG editor by default, but users can install modules to enhance the editing experience.
Accessibility & Customization for Non-Developers
Accessibility and customization options are essential for users who do not have coding experience.
- WordPress: WordPress provides an extensive range of drag-and-drop page builders (such as Elementor and WPBakery) that allow users to design pages without touching code. The theme and plugin ecosystem further expands customization options, making it possible to create unique websites with minimal effort.
- Drupal: While Drupal is highly customizable, it requires more technical knowledge to modify themes and layouts. Unlike WordPress, where most customizations can be done through the admin panel, Drupal often requires adjustments at the code level. However, it offers powerful tools for developers to create highly tailored solutions, especially for enterprise-level sites.
Drupal vs WordPress: Which Offers a Better UX?
For users who prioritize ease of use, quick setup, and intuitive content management, WordPress is the clear winner. Its user-friendly interface, visual editing tools, and extensive plugin support make it accessible to beginners and non-developers.
For users who need a structured, scalable, and developer-friendly CMS with advanced customization options, Drupal provides a more powerful solution. While it comes with a steeper learning curve, its flexibility and content architecture make it a strong choice for complex websites that require high levels of customization and security.
Ultimately, the decision between Drupal vs WordPress depends on the user’s technical expertise and project requirements.
Customization, Flexibility & Functionality
One of the most important aspects of any content management system is its ability to adapt to different website needs. Both platforms offer extensive customization options, but they take different approaches to flexibility and functionality.
Design Options
Themes and templates define the overall look and feel of a website.
- WordPress: Offers a vast selection of themes, both free and premium, available through its official theme repository and third-party marketplaces like ThemeForest and Elegant Themes. Many themes come with built-in customization options, allowing users to tweak colors, layouts, and fonts without touching code. Responsive design is a standard feature, ensuring compatibility across devices.
- Drupal: While Drupal also provides themes, the selection is much smaller compared to its counterpart. Many Drupal themes require manual configuration and are geared toward developers rather than end-users. However, Drupal’s flexibility allows for highly customized designs that cater to specific project requirements.
Extensibility
Both platforms offer ways to extend functionality through add-ons.
- WordPress: Plugins are the foundation of WordPress extensibility. With over 50,000 free plugins in the official directory and thousands more from third-party sources, users can easily add features such as SEO tools, eCommerce functionality, security enhancements, and performance optimizations. The ease of installation makes WordPress highly adaptable to different use cases.
- Drupal: Instead of plugins, Drupal uses modules to extend its core functionality. While the selection is smaller, modules tend to be more developer-focused, offering deeper integrations and advanced customization options. Many essential features, such as multilingual support and content access controls, are built into the core system rather than requiring additional modules.
Advanced Customization
For users who need highly tailored content structures, both platforms offer advanced customization tools.
- WordPress: WordPress provides a user-friendly way to create and manage custom post types, taxonomies, and fields through plugins like Advanced Custom Fields (ACF) and Custom Post Type UI. These allow for flexible content structures without extensive coding.
- Drupal: Drupal is built for complex content management needs. It offers a robust system for defining content types, taxonomies, and custom views. While setting up custom content structures requires more technical expertise, it provides unmatched control over how content is organized and displayed.
Third-Party Integrations & API Support
Connecting a website with external services is essential for modern web development.
- WordPress: WordPress integrates seamlessly with most third-party services, from marketing tools like Mailchimp and HubSpot to eCommerce solutions like WooCommerce and Stripe. It also supports REST API, enabling developers to create custom integrations with external applications.
- Drupal: Drupal is often the preferred choice for large-scale projects requiring deep API integrations. It has built-in API-first capabilities, making it highly effective for headless CMS setups and connecting with external databases, CRMs, and enterprise applications.
Which CMS Offers More Flexibility?
For users who prioritize ease of customization with a vast selection of ready-made themes and plugins, WordPress is the best choice. It provides a balance of design flexibility and user-friendly functionality.
For users who need complete control over content structures, advanced integrations, and a more scalable approach to customization, Drupal is the better option. Although it requires more technical expertise, it delivers superior flexibility for complex web applications.
Performance, Scalability & Hosting

A content management system must not only be functional and flexible but also perform efficiently under different traffic conditions. Performance, scalability, and hosting requirements can significantly impact a website’s speed, reliability, and long-term growth potential.
Speed & Performance Optimization
Fast-loading websites improve user experience and SEO rankings. Both platforms offer performance optimization options but take different approaches.
- One-Click Performance Enhancements: Some platforms provide built-in performance features, while others require manual optimization.
- Caching Strategies: Built-in caching or integration with third-party caching tools can significantly improve site speed.
- Content Delivery Network (CDN) Support: Using CDNs like Cloudflare or Akamai helps load assets faster for global users.
While both systems can achieve excellent speed when optimized correctly, one typically requires more manual configuration than the other.
Scalability
Scalability determines whether a system can handle increased traffic and content complexity.
- Small Websites: Some platforms are better suited for blogs and small business websites due to their lightweight nature and ease of setup.
- Large-Scale Websites: Enterprise applications, government sites, and high-traffic portals need robust scalability features, including optimized database queries, distributed caching, and load balancing.
One system is easier to scale out of the box, while the other requires a more technical approach but provides exceptional performance under heavy load.
Hosting Considerations
Choosing the right hosting solution affects performance, security, and ease of deployment.
- Shared Hosting: Ideal for small sites with minimal traffic but not suitable for complex applications.
- Managed Hosting: Offers pre-configured environments optimized for better speed and security.
- Cloud Hosting & Dedicated Servers: Essential for high-traffic or resource-intensive sites, offering full control over infrastructure.
Some platforms work seamlessly with most hosting providers, while others require specialized hosting environments for optimal performance.
Technical Infrastructure
The underlying technical requirements influence how efficiently a platform operates.
- Server Resources: Some systems run smoothly on minimal server configurations, while others require higher CPU, RAM, and database performance.
- Database Efficiency: Optimized queries and indexing play a key role in how well a site scales with growing content.
- Modular Architecture vs. Lightweight Core: The balance between a streamlined core and extensible functionality affects overall performance.
For businesses and developers choosing a system, understanding the performance, scalability, and hosting implications is crucial to ensuring a smooth and efficient website experience.
Drupal to WordPress Migration
Is Drupal giving your clients a headache? Migrate from Drupal to WordPress with the help of WLA. Learn more about our website migration service offerings.
Security & Stability: Drupal vs WordPress
Website security is a critical concern for businesses, developers, and organizations, especially with the increasing number of cyber threats. In the Drupal vs WordPress debate, both platforms take different approaches to security. While one prioritizes user-friendliness and widespread adoption, the other is built with enterprise-grade security in mind. Understanding their security features, vulnerability management, and community support helps determine which CMS is the best fit for different risk levels.
Built-in Security Features
Security starts with the default features that each CMS offers out of the box.
- WordPress: WordPress provides basic security measures, such as password protection, user roles, and automatic updates for minor releases. However, due to its popularity, it is a frequent target for hackers. Many users rely on third-party security plugins like Wordfence and Sucuri to enhance protection against malware, brute force attacks, and unauthorized access.
- Drupal: Drupal is designed with security at its core, making it a preferred choice for government agencies, large enterprises, and institutions that require strict security compliance. It includes built-in access controls, database encryption, and advanced user permissions. Unlike WordPress, many of its essential security features are integrated directly into the core system, reducing reliance on external plugins.
Vulnerability Management
The way a CMS handles vulnerabilities and security updates determines how well it protects against threats.
- WordPress: Due to its large user base and vast ecosystem of themes and plugins, WordPress sites are often vulnerable to attacks if not properly maintained. Security updates are released frequently, but outdated plugins and themes are common entry points for hackers. Regular monitoring and updates are crucial for WordPress security.
- Drupal: Drupal has a strong reputation for proactive security management. The Drupal Security Team actively reviews and releases patches for vulnerabilities, ensuring the core remains highly secure. Security advisories are published regularly, and updates are strictly tested before release. This approach makes Drupal less prone to attacks, as long as best practices are followed.
Enterprise & Community Support for Security
Both WordPress vs Drupal benefit from active communities and security-focused initiatives, but their structures differ.
- WordPress: The WordPress security community consists of developers, security firms, and plugin creators who contribute to security hardening efforts. However, given the vast number of third-party developers, maintaining consistent security standards across all extensions can be challenging. Enterprise users often rely on managed hosting providers like WP Engine or Kinsta, which offer additional security layers.
- Drupal: Drupal’s security approach is backed by dedicated security teams, external audits, and strict coding standards. The platform follows the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) guidelines and undergoes rigorous security testing. Organizations handling sensitive data, such as government websites and financial institutions, trust Drupal for its stability and enterprise-level security measures.
Drupal vs WordPress: Which CMS is More Secure?
For users who prioritize ease of use but are willing to implement security best practices, WordPress can be made highly secure with proper configuration, regular updates, and security plugins. However, it requires ongoing maintenance to minimize risks.
For businesses and organizations that need a CMS with built-in security, strict access controls, and enterprise-level stability, Drupal is the more secure option. Its proactive security model, robust permission system, and dedicated security team make it a reliable choice for high-risk environments.
Ultimately, the decision between Drupal vs WordPress comes down to security needs. While both platforms can be secured effectively, Drupal’s built-in security features and strict vulnerability management make it the preferred choice for enterprises that require advanced protection.
SEO & Content Optimization: Drupal vs WordPress

Search engine optimization (SEO) plays a crucial role in a website’s visibility and organic traffic. In the Drupal vs WordPress comparison, both platforms offer strong SEO capabilities, but they differ in terms of ease of use and customization.
SEO-Friendly Features
Both WordPress vs Drupal support SEO best practices, but their approaches vary.
- WordPress: SEO is one of WordPress’s strengths, with plugins like Yoast SEO and Rank Math simplifying on-page optimization. These tools provide features such as keyword analysis, XML sitemap generation, and automated meta tags, making SEO accessible for non-technical users.
- Drupal: While Drupal does not have built-in SEO features, it offers modules like Metatag and Pathauto, allowing users to manage metadata and automate URL structures. Drupal’s advanced taxonomy system also makes it easier to organize large volumes of content efficiently.
URL Structure & Metadata Management
URL structure and metadata are essential for search rankings.
- WordPress: WordPress allows users to customize URLs through its permalink settings, ensuring clean and SEO-friendly URLs. SEO plugins further enhance metadata control, allowing users to optimize titles, descriptions, and structured data easily.
- Drupal: Drupal provides deep control over URL aliases, metadata, and canonical tags, but these features require manual configuration. The Redirect module helps manage 301 redirects, improving site structure and search visibility.
Content Organization & Multilingual Support
For websites with extensive content or multiple languages, organization is key.
- WordPress: WordPress supports multilingual content through plugins like WPML and Polylang, making it easy to create and manage translated pages.
- Drupal: Drupal’s built-in multilingual capabilities allow seamless translation of content, menus, and UI elements, making it a strong choice for global websites.
In the Drupal vs WordPress debate, WordPress is ideal for beginners and content-heavy websites, while Drupal provides more granular SEO control for large, structured sites.
Community, Support & Learning Resources
A strong community and access to learning resources are essential for users of any content management system. Both platforms have active ecosystems that provide documentation, forums, and professional support options, but they differ in their approach and accessibility.
Community & Ecosystem
Both platforms have large and engaged communities. One is backed by the world’s largest CMS user base, while the other has a dedicated following of developers and enterprise users. Global meetups, conferences, and online discussions make it easy to find help, share knowledge, and contribute to ongoing development.
Documentation & Training
Extensive documentation is available for both platforms, catering to beginners and advanced users alike. Users can access official guides, free online tutorials, and community-driven forums for troubleshooting and learning. Those looking for structured training can find professional courses, certifications, and webinars designed to help them master different aspects of each system.
Professional Support & Agencies
For businesses that need expert assistance, there are numerous agencies and freelancers specializing in implementation, customization, and ongoing maintenance. Some platforms also offer dedicated support services through managed hosting providers, ensuring better security and performance optimization.
Both systems provide strong support networks, but one offers a more user-friendly learning curve with widespread accessibility, while the other focuses on expert-driven solutions and enterprise-level support. Choosing the right option depends on the level of customization and technical expertise required.
Cost & Total Cost of Ownership
The total cost of a website extends beyond the initial setup and includes long-term expenses such as maintenance, hosting, and infrastructure. Understanding these costs is essential for making an informed decision based on budget and project requirements.
Development & Customization Costs
The initial setup cost varies depending on whether a site is built using pre-designed templates or fully customized. Some platforms offer a vast selection of free and premium themes, making it easier to launch a site with minimal investment. Others require more development work from the start, leading to higher upfront costs for design and functionality. Businesses that need advanced customization may require professional developers, increasing the overall budget.
Maintenance & Update Expenses
Ongoing maintenance includes security updates, bug fixes, and content updates. Some systems rely on frequent third-party updates, which may require additional monitoring and testing. Others provide a more structured update process with built-in security measures, reducing the need for constant oversight. In both cases, hiring a developer or using managed support services can add to long-term expenses.
Hosting & Infrastructure Costs
Hosting costs depend on the website’s traffic and complexity. Basic sites can run on shared hosting with minimal expenses, while larger, high-traffic websites require dedicated or cloud hosting for optimal performance. Some platforms work efficiently on standard hosting providers, while others may need specialized hosting environments, increasing infrastructure costs.
Balancing development, maintenance, and hosting expenses is key to determining the best long-term solution for a website’s needs.
Ideal Use Cases & Business Considerations
Choosing the right content management system depends on the specific needs of a business, including budget, scalability, and technical expertise. Each platform excels in different scenarios, making it essential to align requirements with the strengths of the system.
When to Choose a More User-Friendly CMS
For small to medium-sized businesses, personal blogs, and simple eCommerce stores, a user-friendly CMS is often the best choice. It provides an intuitive interface, a vast selection of themes and plugins, and a straightforward setup process. Businesses looking for quick deployment and easy content management without heavy development work will benefit from this option.
When to Choose a More Advanced CMS
Organizations that require a scalable, high-security solution should consider a more advanced CMS. It is well-suited for government agencies, large corporations, universities, and enterprises that need complex content structures, multi-user permissions, and deep customization. While it has a steeper learning curve, it offers extensive flexibility and control, making it ideal for technically demanding projects.
Aligning Business Needs with Platform Strengths
The choice should be guided by a balance of budget, technical expertise, and long-term scalability. Businesses with limited resources and a need for simplicity should opt for a platform that minimizes development costs and maintenance overhead. Those with dedicated technical teams and specialized requirements will benefit from a more customizable and robust system. Understanding these factors ensures a well-informed decision that supports future growth.
Website as a service
Website As a Service [WAAS] provides complete website solutions including design, hosting, and maintenance through a convenient subscription model for Agencies.
Future Outlook & Trends
The landscape of content management is constantly evolving, with new features, technologies, and community-driven innovations shaping the future. Understanding where each platform is headed helps businesses and developers make long-term decisions.
Upcoming Features & Roadmaps
Both platforms continue to release updates focused on performance, security, and user experience. Future developments emphasize improved editing interfaces, better integration with modern development frameworks, and enhanced scalability. One platform is refining its block-based editing experience, making it more intuitive, while the other is enhancing its structured content capabilities to support even more complex digital experiences.
Community and Ecosystem Developments
Community-driven contributions play a significant role in the growth of each system. Open-source development ensures that new third-party tools, integrations, and frameworks are introduced regularly. Trends indicate a stronger push toward automation, artificial intelligence-powered content management, and API-driven flexibility for headless applications. Increased collaboration with cloud service providers and enterprise solutions is also shaping the ecosystem’s future.
Long-Term Viability
As digital experiences become more dynamic, adaptability is key. One system’s widespread adoption and ease of use position it as a long-term choice for small businesses and growing enterprises. The other, with its focus on structured data and security, remains a go-to option for large-scale and high-security environments. Both platforms continue to evolve, ensuring they remain competitive and capable of meeting the changing demands of modern web development.
Final Verdict & Recommendations
Choosing the right content management system depends on factors such as ease of use, scalability, security, and customization needs. While both options are powerful, they cater to different audiences and project requirements.
One platform is known for its user-friendly interface, extensive theme and plugin ecosystem, and quick setup, making it ideal for small to medium-sized businesses and content-driven websites. The other is built for flexibility, security, and complex site structures, making it the preferred choice for enterprise-level organizations, government agencies, and institutions that require advanced customization.
To determine the best fit, consider the following:
- Technical Expertise – If ease of use and minimal coding are priorities, one platform is the better choice. If a high level of technical customization is required, the other is more suitable.
- Scalability & Complexity – Simple websites with moderate traffic can function well with an easy-to-use CMS, while large-scale, high-security sites benefit from a more robust framework.
- Budget & Maintenance – Initial development costs, ongoing updates, and hosting requirements should align with the available resources.
For users seeking a straightforward, cost-effective solution with a low learning curve, an accessible CMS is the best option. For developers, enterprises, and organizations handling complex workflows and security-sensitive data, a more advanced system provides the control and scalability needed for long-term growth. Making the right choice ensures a smoother web development experience and long-term success.

Drupal vs WordPress – Which One is Right for You?
The “Drupal or WordPress” debate comes down to understanding the specific needs of a website. Throughout this guide, we’ve explored how each platform performs in terms of usability, customization, security, scalability, and cost. While one excels in simplicity and accessibility, the other offers unmatched flexibility and security for complex projects.
When comparing WordPress vs Drupal, it’s clear that each serves a distinct audience. One is ideal for small businesses, bloggers, and startups looking for a quick and easy website setup with extensive plugin support. The other is built for developers, enterprises, and institutions requiring advanced control, high security, and structured content management. The right choice
Before making a final decision in the Drupal vs WordPress debate, it’s essential to explore both platforms, test their features, and consider expert guidance. If you’re leaning toward WordPress, but want a scalable and professionally managed solution, White Label Agency can help. Our expert team specializes in WordPress development, ensuring you get a fully optimized, high-performing website tailored to your needs. Get in touch today to explore our WordPress services and take your website to the next level!






