- WordPress Web Design Agency
- What Are Monochromatic Colors?
- The Psychology Behind Monochromatic Colors
- Benefits of Monochromatic Colors in Web Design
- Successful Monochromatic Colors Examples in Web Design
- Best Practices for Monochromatic Web Design
- How do you make a Monochromatic color scheme?
- Tools and Resources for Designing Monochromatic Schemes
- What mood do Monochromatic Colors have?
- Hire a WordPress Designer
- The Power of Monochromatic Design: Final Thoughts
- Ready to Transform Your Website?
- FAQs
Look at Apple’s website, with its masterful play of whites, grays, and blacks, or Spotify’s artist pages bathed in various shades of green. These aren’t random choices – they’re perfect examples of monochromatic color schemes at work. A monochromatic color scheme uses a single base color in different shades, tints, and tones to create a cohesive design that’s both sophisticated and visually appealing.
In this guide, we’ll explore why leading brands choose monochromatic colors for their web designs, how to implement them effectively, and what tools you can use to create your own stunning monochromatic palette. Whether you’re a web designer, developer, or brand manager, you’ll learn practical strategies to enhance user experience and brand aesthetics using this powerful design approach.
WordPress Web Design Agency
Partner with our white label WordPress web design agency for custom, scalable solutions. We design, develop, and maintain websites tailored to your clients.
What Are Monochromatic Colors?
A monochromatic color scheme is a mix of one base hue (color) and its variations created by adjusting brightness, saturation, and intensity. It is a single color and explored in all its possible expressions – from its lightest to its darkest versions.
Key components of monochromatic color schemes are:
- Hue is your base color (like blue, red, or yellow)
- Tints are created by adding white to your base hue, making it lighter
- Shades are made by adding black, creating darker versions
- Tones emerge when adding gray, which reduces the color’s intensity
These variations work together to create depth and visual interest while maintaining harmony. For instance, if you choose blue as your base color, your palette might include pale sky blue tints, deep navy shades, and muted denim-like tones.
Contrast with other color schemes:
- Complementary Schemes: Use colors opposite each other on the color wheel (e.g., red and green).
- Analogous Schemes: Use colors adjacent to each other on the color wheel (e.g., blue, blue-green, and green).
- Triadic Schemes: Use three colors evenly spaced around the color wheel (e.g., red, yellow, and blue).
- Polychromatic Schemes: Use multiple colors from different points on the color wheel, including primary, secondary, and tertiary colors, to create a vibrant and diverse palette.
The Psychology Behind Monochromatic Colors
Base color choice sets the emotional foundation of the design. Every shade, tint, and tone builds upon this foundation to create a specific psychological impact on users. This is where color theory plays a crucial role, as it helps designers understand how different hues and their variations influence emotions and behaviors.
Trust and Professionalism: Blue
Blue, the color favored by tech giants and financial institutions, creates an instant feeling of trust and reliability. When you use different shades of blue, from light sky blue to deep navy, you maintain that trustworthy feel while adding visual depth.
Example: Facebook and LinkedIn leverage this psychology masterfully in their designs.
Energy and Urgency: Red
Red commands attention and creates urgency. From soft pink tints to deep burgundy shades, red’s monochromatic color schemes can convey anything from gentle warmth to intense passion.
Example: Netflix uses this to its advantage, combining dark red shades for drama with lighter tints for contrast.
Digital and Dystopian: Green
The Matrix revolutionized how monochromatic color schemes can create an atmosphere in visual media. Its distinctive green-tinted digital world influenced countless web designs in the tech sector.
Example: The movie’s iconic green monochromatic palette has inspired many cybersecurity and tech websites, using various shades of green to create a digital, tech-focused atmosphere.

Creating Specific Moods
Want to create a luxurious feel? Consider using neutral monochromatic color schemes – varying shades of gray, black, or white create an inherent sense of elegance.
Example: Apple’s website is the perfect example of this approach.
For a minimalist look, stick to lighter tints of any color. Or create drama with darker shades of bold colors like purple or red.
Benefits of Monochromatic Colors in Web Design
Simplified Design Process
Working with monochromatic colors makes web designer’s decisions straightforward and efficient. Instead of juggling multiple colors, they can perfect variations of one hue. With fewer colors to manage, designers can quickly experiment with layouts, typography, and imagery.
Enhanced Brand Recognition
Want your brand to be as instantly recognizable as Coca-Cola’s red? That’s exactly what monochromatic design can do for you. By mastering variations of your core brand color, you’ll build a visual identity that users remember.
Practical Advantages
Content First: With a monochromatic palette, content gets all the attention it deserves. No distracting color combinations – just clean, focused design that puts the message front and center.
Flexibility: From sleek minimalism to bold statements, monochromatic schemes adapt to web designers’ needs. Plus, they stay relevant year after year, unlike trendy color combinations that can quickly feel outdated.
Successful Monochromatic Colors Examples in Web Design
Apple: Mastering Minimalism
Apple’s website proves that black, white, and grays aren’t boring – they’re sophisticated. Their monochromatic approach:
- Creates a premium feel
- Lets product images pop
- Maintains focus on key features
Spotify: Green Done Right
Spotify’s artist pages show how to rock a single color. Their green palette:
- Creates an immersive experience
- Keeps brand recognition strong
- Makes album artwork stand out

Tiffany & Co.: The One Color
That signature Tiffany blue? It’s not just a color – it’s an empire. Their monochromatic approach:
- Creates instant brand recognition
- Conveys luxury and exclusivity
- Works seamlessly across all platforms
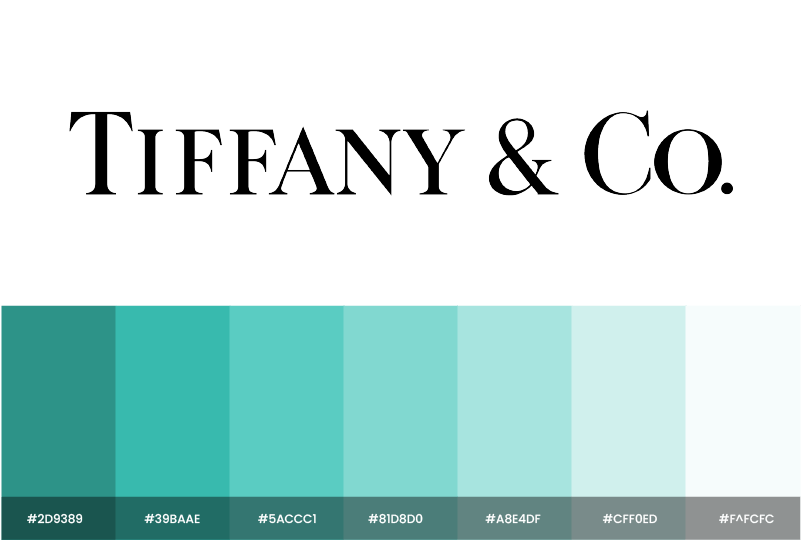
Best Practices for Monochromatic Web Design
Creating stunning monochromatic websites requires careful consideration of several key elements. Here’s how to nail the execution:
Start With the Perfect Base Color
The foundation of any monochromatic design is its base color. It should:
- Match the brand’s personality and values
- Create the right emotional connection with users
- Work well across digital platforms
Example: A wellness brand might choose a calming sage green, while a tech startup could opt for an energetic electric blue.
Build Visual Hierarchy
Never let monochrome mean flat. Create depth by:
- Using darker shades for primary elements like headers
- Applying lighter tints for backgrounds and secondary content
- Adding medium tones for supporting elements
Pro tip: Maintain a contrast ratio of at least 4.5:1 between text and background colors for optimal readability.
Add Texture and Pattern
Keep the design interesting without breaking the color scheme:
- Incorporate subtle gradients
- Use patterns in varying shades
- Add shadow effects for depth
Example: A luxury jewelry website might use a pattern of light gold geometric shapes against a slightly darker gold background.
Prioritize Accessibility
Great design works for everyone:
- Test color combinations with accessibility tools
- Ensure text remains readable across all shades
- Include alternative visual cues beyond color
Pro tip: Tools like WebAIM’s contrast checker can help validate color choices for accessibility compliance.
The key to successful monochromatic color scheme design lies in a balance – between simplicity and interest, between brand identity and user experience.
How do you make a Monochromatic color scheme?
Creating a monochromatic color scheme involves using variations of a single color by adjusting its tint, tone, and shade. Here’s how you can build one:
1. Choose a Base Color
- Pick one hue from the color wheel. For example, blue.
2. Create Variations of the Base Color
- Tints: Lighten the base color by adding white (e.g., sky blue).
- Shades: Darken the base color by adding black (e.g., navy blue).
- Tones: Muting the base color by adding gray (e.g., slate blue).
3. Use a Balance of Light and Dark
- Incorporate different light, medium, and dark versions of your color to add contrast and depth.
4. Add Neutral Colors (Optional)
- If needed, use black, white, or gray for balance without disrupting the monochromatic effect.
5. Apply to Your Design
- Whether in art, interior design, or digital graphics, use the lighter shades for highlights, medium tones for the main elements, and darker shades for depth and contrast.
By following these steps, you can create a cohesive and visually appealing monochromatic color scheme for your artwork or designs.
Tools and Resources for Designing Monochromatic Schemes
Paletton
- What It Does: A color scheme designer that helps web designers create monochromatic color palettes with adjustable saturation and lightness.
- Why It’s Useful: Provides a visual preview of how the palette will look in a design.
- Link: Paletton
Adobe Color
- What It Does: A powerful color palette generator that allows you to create monochromatic color schemes by selecting a base color and generating tints, shades, and tones.
- Why It’s Useful: Integrates seamlessly with Adobe Creative Cloud apps like Photoshop and Illustrator.
- Link: Adobe Color
Coolors
- What It Does: A user-friendly color palette generator that lets you create, save, and export monochromatic color palettes.
- Why It’s Useful: Offers quick adjustments and inspiration for monochromatic designs.
- Link: Coolors
HSL Color Picker
- What It Does: A simple tool for generating monochromatic colors using the HSL (Hue, Saturation, Lightness) model.
- Why It’s Useful: Helps designers fine-tune tints, shades, and tones for monochromatic color schemes.
- Link: HSL Color Picker
Color Oracle
- What It Does: A color blindness simulator that shows how your monochromatic design appears to users with color vision deficiencies.
- Why It’s Useful: Helps ensure your design is inclusive and accessible.
- Link: Color Oracle
What mood do Monochromatic Colors have?
The mood of a monochromatic color scheme depends on the base color used. Since it consists of variations of a single hue, it creates a harmonious and unified feel. Here’s how different colors influence mood:
1. Calm & Soothing – Blues & Greens
- Blue monochromatic schemes feel tranquil, professional, and trustworthy (often used in corporate branding).
- Green schemes evoke growth, renewal, and a connection to nature (common in wellness and eco-friendly designs).
2. Warm & Energetic – Reds, Oranges, & Yellows
- Red monochrome can feel bold, passionate, and intense (often used in marketing and art).
- Orange feels friendly and energetic, while yellow conveys happiness and warmth.
3. Elegant & Sophisticated – Purples & Neutrals
- Purple creates a luxurious, mysterious, or creative mood.
- Brown and beige tones feel earthy, cozy, and inviting.
4. Minimalist & Modern – Grayscale (Black, White, and Gray Tones)
- Monochromatic grayscale schemes give a timeless, sophisticated, and modern feel, often seen in photography and minimalist design.
Overall Impact of Monochromatic Colors:
- Creates visual unity and avoids clashing colors.
- Can feel soothing and balanced, making it ideal for branding, design, and art.
- The mood can shift depending on contrast and brightness—high contrast feels bold, while softer variations feel subtle and calming.
Hire a WordPress Designer
Discover the benefits of choosing to hire a WordPress designer. Enjoy focused attention, quick turnaround, cost-effectiveness, and expert design for the projects.
The Power of Monochromatic Design: Final Thoughts
Monochromatic color design isn’t just another passing trend – it’s a proven strategy for creating websites that make an impact. From Apple’s sophisticated grays to Spotify’s vibrant greens, leading brands show how powerful a well-executed monochromatic colors palette can be.
What makes the monochromatic design stand out:
- Creates instant visual recognition
- Delivers a seamless user experience
- Maintains timeless appeal
- Adapts to any brand personality
The beauty of monochromatic design lies in its versatility. Whether the goal is minimalist elegance or bold drama, the right monochromatic palette can achieve it – all while maintaining professional polish and user-friendly navigation.
Ready to Transform Your Website?
At the White Label Agency, our dedicated web designers specialize in creating stunning monochromatic websites, whether you’re starting fresh or redesigning an existing site, we’ll help you leverage the power of monochromatic web design.
Let’s create something extraordinary together. Contact us today to explore how we can elevate your digital presence with professional monochromatic web design.
FAQs
What is the meaning of monochromatic in art?
In art, monochromatic refers to a color scheme that consists of different shades, tints, and tones of a single color. This approach creates a harmonious and visually cohesive look by using variations of one hue.
For example, a monochromatic painting in blue might include navy, sky blue, and pastel blue, all derived from the same base color. Artists use monochromatic schemes to emphasize composition, texture, and contrast without the distraction of multiple colors.
This technique is popular in design, photography, and interior decor for its simplicity and elegance.
Can monochromatic be black and white?
Technically, black and white is not considered a true monochromatic color scheme because it involves two opposing shades—black (absence of color) and white (presence of all colors in light theory). However, in certain contexts, black, white, and grayscale variations are sometimes loosely referred to as monochrome (especially in photography and printing).
A true monochromatic color scheme consists of different shades, tints, and tones of a single hue. For example, a blue monochromatic scheme would use variations like navy, sky blue, and pastel blue.
So, while black and white images are often called monochrome, in the strictest artistic sense, monochromatic refers to variations of one color rather than the entire grayscale spectrum.
Why should we avoid a monochromatic color scheme?
While a monochromatic color scheme can create a cohesive and visually appealing design, it does have some limitations that make it less ideal in certain situations. Here’s why you might want to avoid it:
1. Lack of Contrast & Visual Interest
Using only one color (with different tints and shades) can make a design look flat and unexciting.
Limited contrast can make it hard to distinguish elements, especially in web design and UI/UX.
2. Can Feel Monotonous or Boring
Without accent colors, a monochromatic scheme might lack dynamism and fail to capture attention.
Overuse of a single color can feel repetitive and uninspired if not balanced with textures, patterns, or different saturation levels.
3. Difficult for Accessibility & Readability
Low-contrast monochrome designs can reduce readability, making text hard to read, especially for visually impaired users.
It may fail color contrast ratio guidelines, making it problematic for websites and branding.
4. Limited Emotional Range
A single-color scheme may not fully convey complex emotions or diverse brand messaging.
For example, red alone might feel too aggressive, and blue might be too calm for an energetic brand.
5. Can Be Harder to Match Across Different Mediums
Different screens, printers, and materials may render shades inconsistently, making it harder to maintain color consistency.
Solution:
If you like the idea of a monochromatic scheme but want more variety, consider using analogous colors (neighboring colors on the color wheel) or adding a complementary accent color to make the design more engaging.
Why is it called monochromatic?
The term monochromatic comes from the Greek words:
“Mono” (μόνος) – meaning “one” or “single.”
“Chroma” (χρῶμα) – meaning “color” or “hue.”
So, monochromatic literally means “one color.”
In art, design, and color theory, a monochromatic color scheme consists of different tints, shades, and tones of a single base color. This means that instead of using multiple hues, the design or artwork relies on variations of just one color by adding:
White (to create tints – lighter versions of the color).
Black (to create shades – darker versions of the color).
Gray (to create tones – muted versions of the color).
This results in a cohesive, harmonious, and often elegant visual effect. Monochromatic schemes are commonly used in minimalistic designs, branding, photography, and fine art to create depth and mood without introducing multiple colors.







